【特惠】26考研
红包
【考研】专业课HOT
26考研
【MBA】在职考研
【规划】择校备考
【报录比】查询
计划
【真题】全套解析
资料
【申硕】同等学力
预备
【大纲】5500词汇
免费
【在线】英语测评
免费
【大纲】最新大纲
精

扫码加入训练营
牢记核心词
学习得礼盒
2015考研英语翻译平时需要考研考生们做大量的练习,多练多积累、分析句型累计词汇,才能在考研英语翻译中获得高分,新东方在线小编整理了2015考研英语翻译练习及答案,希望对大家有所帮助。
请翻译划线语句
A study of more than 5,000 children in Southern California found that those kids who lived within 250 feet (76 meters) of busy roads had a 50% higher risk of having had asthma symptoms in the past year. The researchers found that the asthma risk decreased to normal for children living about 600 feet or more away from a busy road. The greatest risk of asthma symptoms was found in children who had lived near busy roads since before age 2.
①Asthma is a disease of the human respiratory system in which the airways narrow, often in response to a "trigger" such as exposure to an allergen, cold air, exercise, or emotional stress.This narrowing causes symptoms such as wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing, which are the hallmarks of asthma. Between episodes, most patients feel fine.
The disorder is a chronic inflammatory condition in which the airways develop increased responsiveness to various stimuli, characterized by bronchial hyper-responsiveness, inflammation, increased mucus production, and intermittent airway obstruction. The symptoms of asthma, which can range from mild to life threatening, can usually be controlled with a combination of drugs and lifestyle changes.
Public attention in the developed world has recently focused on asthma because of its rapidly increasing prevalence, affecting up to one in four urban children.②Susceptibility to asthma can be explained in part by genetic factors, but no clear pattern of inheritance has been found. ③Asthma is a complex disease that is influenced by multiple genetic, developmental, and environmental factors, which interact to produce the overall condition.
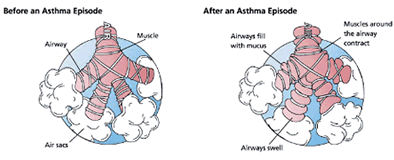
④During an asthma episode, inflamed airways react to environmental triggers such as smoke, dust, or pollen. The airways narrow and produce excess mucus, making it difficult to breathe.
A typical inhaler, of Serevent (salmeterol)Symptomatic control of episodes of wheezing and shortness of breath is generally achieved with fast-acting bronchodilators. These are typically provided in pocket-sized, metered-dose inhalers (MDIs—see the image to the right). In young sufferers, who may have difficulty with the coordination necessary to use inhalers, or those with a poor ability to hold their breath for 10 seconds after inhaler use (generally the elderly), an asthma spacer is used. The spacer is a plastic cylinder that mixes the medication with air in a simple tube, making it easier for patients to receive a full dose of the drug (see top image) and allows for the active agent to be dispersed into smaller, more fully inhaled bits. A nebulizer—which provides a larger, continuous dose—can also be used. Nebulizers work by vapourizing a dose of medication in a saline solution into a steady stream of foggy vapor, which the patient inhales continuously until the full dosage is administered. There is no clear evidence, however, that they are more effective than inhalers used with a spacer. Nebulizers may be helpful to some patients experiencing a severe attack. ⑤Such patients may not be able to inhale deeply, so regular inhalers may not deliver medication deeply into the lungs, even on repeated attempts. Since a nebulizer delivers the medication continuously, it is thought that the first few inhalations may relax the airways enough to allow the following inhalations to draw in more medication.Since a nebulizer delivers the medication continuously, it is thought that the first few inhalations may relax the airways enough to allow the following inhalations to draw in more medication.
new words
respiratory system 呼吸系统
The respiratory system is the biological system of any organism that engages in gas exchange. Even trees have respiratory systems, taking in carbon dioxide and emitting oxygen during the day, consuming carbon dioxide and producing oxygen constantly.
hallmarks 外表
A mark indicating quality or excellence.
symptom 症状
A symptom may loosely be said to be a physical condition which shows that one has a particular illness or disorder (see e.g. Longman, 1995). An example of a symptom in this sense of the word would be a rash. However, correctly speaking, this is known as a sign, as would any indication detectable by a person other than the sufferer in the absence of verbal information from the patient.
dyspnea 呼吸困难
Dyspnea (Latin dyspnoea, Greek dyspnoia from dyspnoos - short of breath) or shortness of breath (SOB) is perceived difficulty breathing or pain on breathing. It is a common symptom of a great many disorders.
epidemiology 流行病学
In epidemiology, the prevalence of a disease in a statistical population is defined as the ratio of the number of cases of a disease present in a statistical population at a specified time and the number of individuals in the population at that specified time.
Genetics 遗传学
Humans began applying knowledge of genetics in prehistory with the domestication and breeding of plants and animals. In modern research, genetics provides important tools for the investigation of the function of a particular gene, e.g., analysis of genetic interactions. Within organisms, genetic information generally is carried in chromosomes, where it is represented in the chemical structure of particular DNA molecules.
Inheritance 遗传
Inheritance is the practice of passing on property, titles, debts, and obligations upon the death of an individual. It has long played an extremely important role in human societies.
hypersensitivity 过敏性
Hypersensitivity is an immune response that damages the body's own tissues.
spasm 抽搐, 痉挛
A spasm is a sudden, involuntary contraction of a muscle, a group of muscles, or a hollow organ, or a similarly sudden contraction of an orifice. A spasm is usually accompanied by a sudden burst of pain.
Inflammation 炎症
Inflammation is the first response of the immune system to infection or irritation and may be referred to as the innate cascade. Inflammation is characterized by the following quintet: redness (rubor), heat (calor), swelling (tumor), pain (dolor) and dysfunction of the organs involved (functio laesa).
mucus 黏液
Mucus is a slippery secretion of the lining of various membranes in the body (mucous membranes). Mucus aids in the protection of the lungs by trapping foreign particles that enter the nose during normal breathing. Additionally, it prevents tissues from drying out.
bronchodilator 支气管扩张
A bronchodilator is a medication intended to improve bronchial airflow. Treatment of bronchial asthma is the most common application of these drugs. They are also intended to help expand the airways and improve the breathing capacity of patients with emphysema, pneumonia and bronchitis.
inhaler 吸入器
An inhaler is a medical device used for delivering medication into the body via the lungs. It is often used in the treatment of asthma
nebulizer 喷雾器
In medicine, a nebulizer is a device used to administer medication to people in forms of a liquid mist to the airways. It is thus used in treating respiratory diseases. Also called "atomizers", they pump air or oxygen through a liquid medicine to turn it into a vapor, which is then inhaled by the patient.
【英语翻译】资料这里有↑↑↑

添加班主任领资料
添加考研班主任
免费领取考研历年真题等复习干货资料

 推荐阅读
推荐阅读
为了让考研的同学更高效地复习考研英语,新东方在线考研频道整理了2026考研英语翻译的三个过程,考研的同学可以了解一下,希望对大家有所帮助。
为了让考研的同学更高效地复习考研英语,新东方在线考研频道整理了2026考研英语翻译选词要多样化,考研的同学可以了解一下,希望对大家有所帮助。
为了让考研的同学更高效地复习考研英语,新东方在线考研频道整理了2026考研英语翻译用词要简洁有力,考研的同学可以了解一下,希望对大家有所帮助。
为了让考研的同学更高效地复习考研英语,新东方在线考研频道整理了2026考研英语翻译用词要通俗易懂,考研的同学可以了解一下,希望对大家有所帮助。
为了让考研的同学更高效地复习考研英语,新东方在线考研频道整理了2026考研英语翻译选词要贴切,考研的同学可以了解一下,希望对大家有所帮助。

 资料下载
资料下载
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
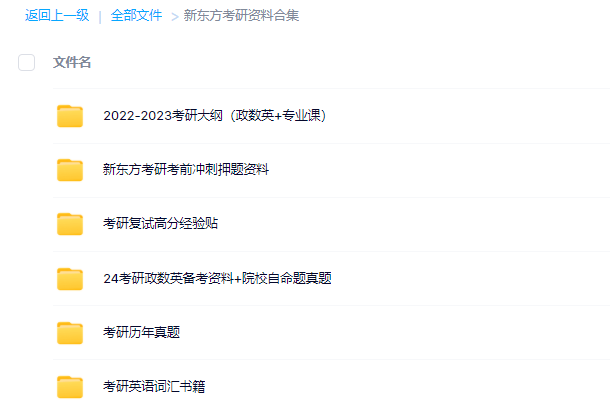
新东方在线考研资料合集
下载方式:微信扫码,获取网盘链接

目录:
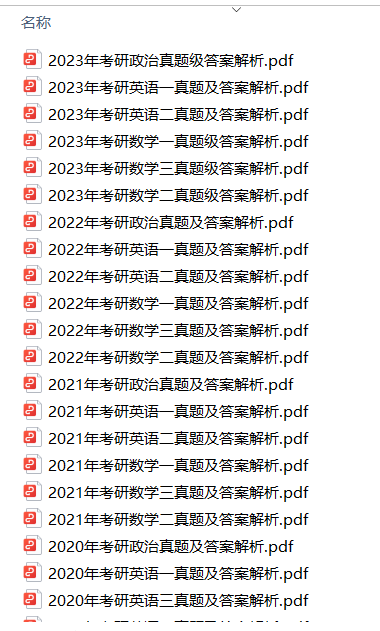
1.2013-2023年近10年政数英真题及解析PDF版(新东方)
2.2013-2023年专业课考试历年真题及解析PDF版
3.24考研复习备考资料大合集:大纲+备考资料+词汇书+考前押题+自命题
资料介绍:
1.2013-2023年近10年政数英真题及解析PDF版(新东方)
 、
、
2.2013-2023年专业课考试历年真题及解析PDF版
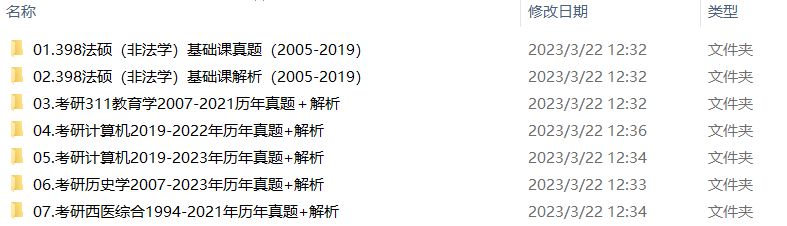
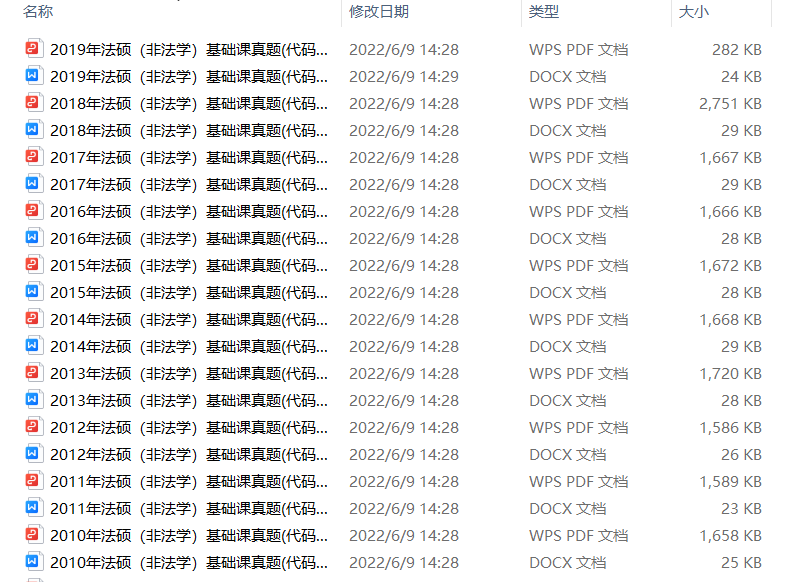
3.24考研复习备考资料大合集
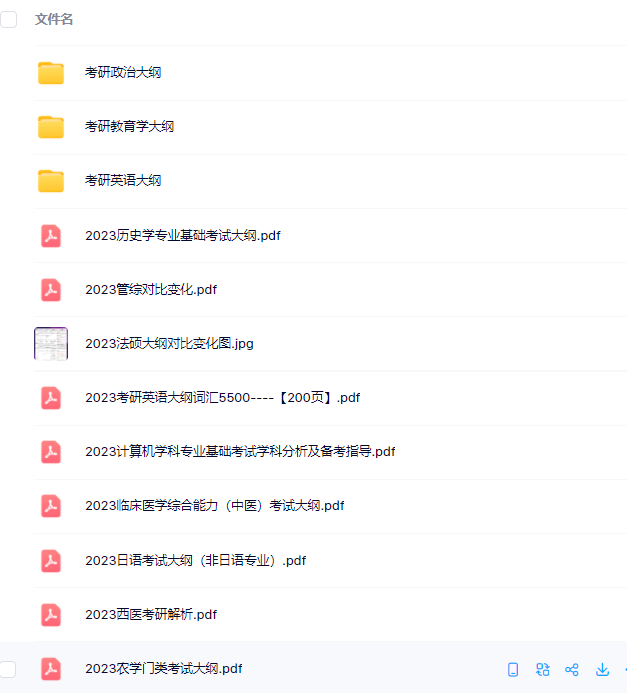
3.24考研复习备考资料:考研大纲
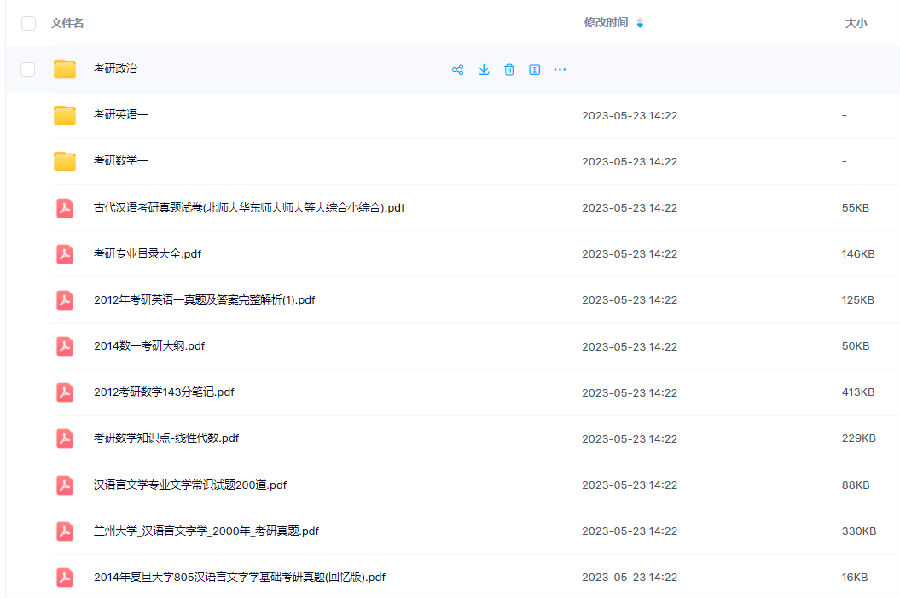
3.24考研复习备考资料:政数英备考资料+自命题真题
------------------
考研备考过程中,尤其是专业课部分,参考往年的考试真题,对于我们的复习有更好的帮助。北京大学考研真题资料都有哪些?小编为大家进行了汇总。
北京大学考研真题资料-公共课
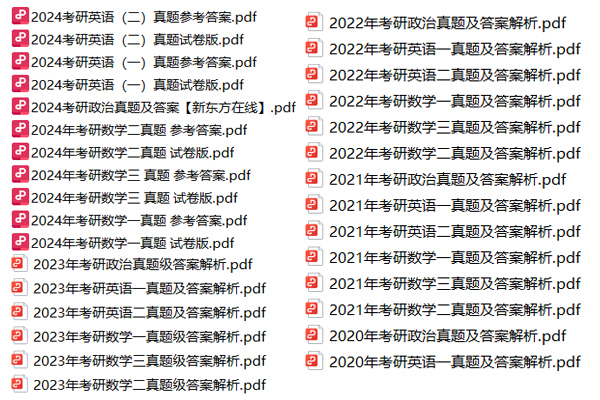
北京大学考研真题资料-专业课


以上就是关于“北京大学考研真题资料下载(历年汇总)”的整理,更多考研资料下载,请关注微信获取下载地址。
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包

 阅读排行榜
阅读排行榜
 相关内容
相关内容