特惠-26考研冲刺
特惠-27考研课
双证-在职硕士
免联考-同等学力
复试分数线
26复试全面指导
模拟复试面试
26考研-全套真题
26考研估分
保研-路线图
27考研-智能择校
27考研-英语测评
27考研-新大纲对比
热门-计算机择校

扫码加入训练营
牢记核心词
学习得礼盒
But climate, however critical, is only part of the problem, scientists say. A growing body of evidence suggests that other human activity and policy have at least as much impact on wildfires as climate change. To effectively address a longer and more intense wildfire season – and ensure the safety of residents in fire-prone areas – both environmental and human factors have to be taken into account in more holistic ways, they say.
That means more than just sweeping dry brush off the front porch. Though such steps are an important part of the process, officials and researchers alike are calling for a comprehensive approach to wildfires: one that incorporates fire safety and behavior in key policy decisions and legislation. Such an effort would also recognize that fire can be helpful as well as harmful and embrace fire’s place in human society.
“We need not just a policy shift but also a cultural shift in the dialogue around fires in our landscape and how to manage them,” says Jennifer Balch, director of Earth Lab and a professor of geography at the University of Colorado in Boulder. “Fire is not something we can remove. A large majority of the country is living in fire-prone areas. How do we live with wildfire? How do we manage?”
“More and more researchers are arguing that anthropogenic influences are really important [to understanding wildfires],” adds Max Moritz, a specialist in fire ecology and management and a professor at the College of Natural Resources at the University of California, Berkeley. “By leaving them out we’re missing a critical piece of the solution.”
Changing attitudes on fire
选取部分:
Though often viewed as a problem for western states, the growing frequency of wildfires is a national concern because of its impact on federal tax dollars, Professor Moritz and others say.
In 2015, the US Forest Service for the first time spent more than half of its $5.5 billion annual budget fighting fires – nearly double the percentage it spent on such efforts 20 years ago. In effect, fewer federal funds today are going towards the agency’s other work – such as forest conservation, watershed and cultural resources management, and infrastructure upkeep – that affect the lives of all Americans.
Another nationwide concern is whether public funds from other agencies, such as the Department of Housing and Urban Development, are going into construction in fire-prone districts. As Moritz puts it, how often are federal dollars building homes that are likely to be lost to a wildfire?
【英语一二真题】资料这里有↑↑↑
本文关键字: 2017考研英语二阅读文章源文

 资料下载
资料下载
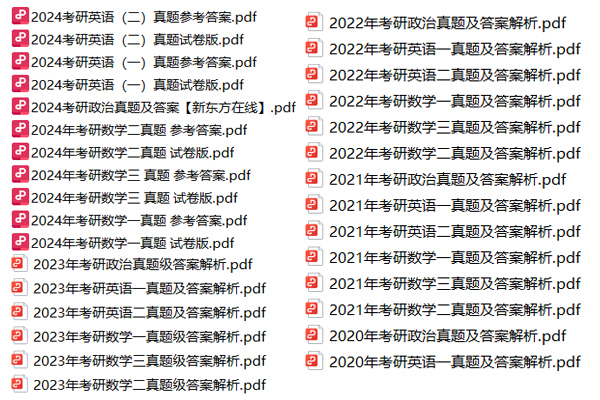
2014年-2025年考研历年真题汇总
发布时间:2024-04-25扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
考研大纲PDF电子版下载-历年(附解析)
发布时间:2024-04-25扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
2026年考研政数英备考资料zip压缩包
发布时间:2024-04-25扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
考研英语大纲词汇5500打印版(基础必备)
发布时间:2024-04-25扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
新东方在线考试模拟题【12套】
发布时间:2024-04-25扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
2026年考研专业课知识点总结
发布时间:2024-04-25扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
新东方考研资料下载地址
发布时间:2023-05-17新东方在线考研资料合集
下载方式:微信扫码,获取网盘链接

目录:
1.2013-2023年近10年政数英真题及解析PDF版(新东方)
2.2013-2023年专业课考试历年真题及解析PDF版
3.24考研复习备考资料大合集:大纲+备考资料+词汇书+考前押题+自命题
资料介绍:
1.2013-2023年近10年政数英真题及解析PDF版(新东方)
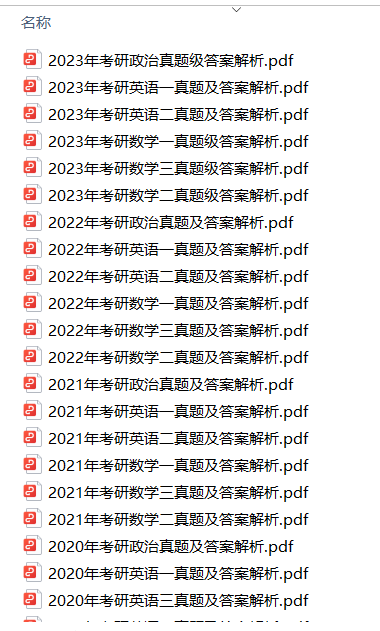 、
、
2.2013-2023年专业课考试历年真题及解析PDF版
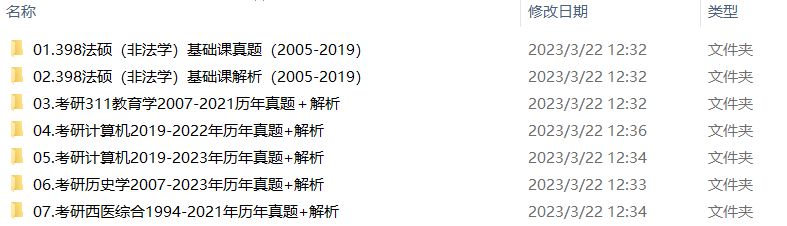
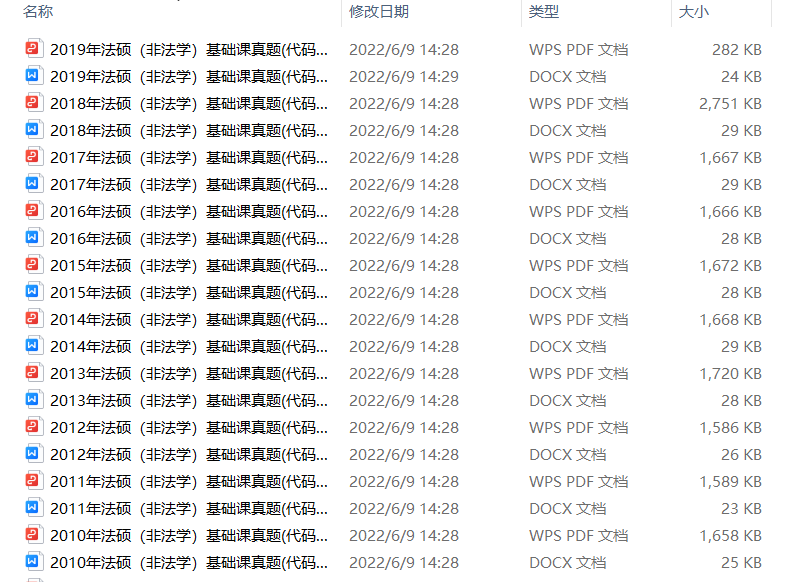
3.24考研复习备考资料大合集
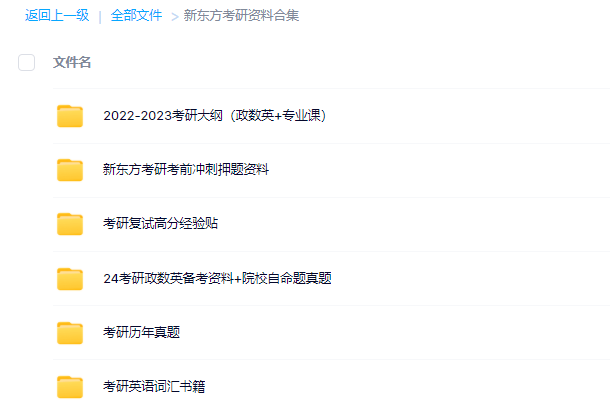
3.24考研复习备考资料:考研大纲
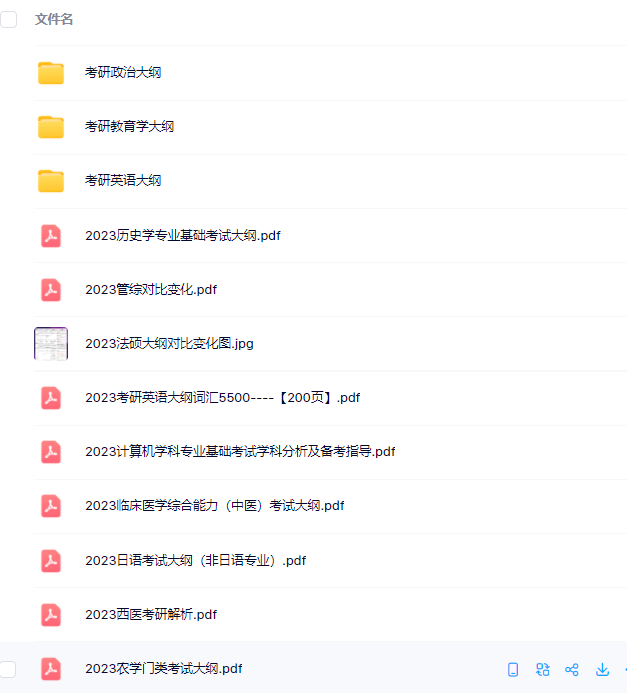
3.24考研复习备考资料:政数英备考资料+自命题真题
------------------
考研备考过程中,尤其是专业课部分,参考往年的考试真题,对于我们的复习有更好的帮助。北京大学考研真题资料都有哪些?小编为大家进行了汇总。
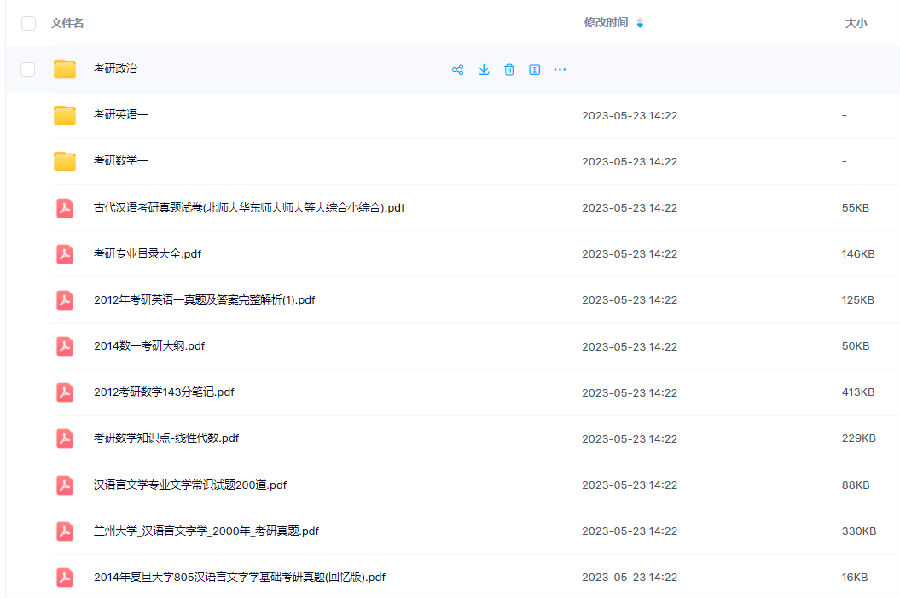
北京大学考研真题资料-公共课
北京大学考研真题资料-专业课


以上就是关于“北京大学考研真题资料下载(历年汇总)”的整理,更多考研资料下载,请关注微信获取下载地址。
2024考研公共课必背知识点汇总
发布时间:2023-01-03扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
2013-2023考研历年真题汇总
发布时间:2023-01-03扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
考研英语大纲词汇(PDF可打印)
发布时间:2023-01-03扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
2024考研专业课知识点总结
发布时间:2023-01-03扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
2023考研政治 内部押题 PDF
发布时间:2022-11-16扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
徐涛:23考研预测六套卷
发布时间:2022-11-16扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
考研政数英冲刺资料最新整理
发布时间:2022-11-16扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
23考研答题卡模板打印版
发布时间:2022-11-16扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
2023考研大纲词汇5500PDF电子版
发布时间:2022-07-28扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
考研历年真题(公共课+专业课)
发布时间:2022-07-28扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
考研英语阅读100篇附解析及答案
发布时间:2022-01-07扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
新东方考研学霸笔记整理(打印版)
发布时间:2022-01-07扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
2001-2021年考研英语真题答案(可打印版)
发布时间:2022-01-07扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
考研英语词汇5500(完整版下载)
发布时间:2022-01-07扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
2022考研政审表模板精选10套
发布时间:2022-01-07扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
历年考研真题及答案 下载
发布时间:2021-12-09扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
考研政审表模板汇总
发布时间:2020-06-17扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
近5年考研英语真题汇总
发布时间:2020-06-17扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
考研英语大纲词汇5500
发布时间:2020-06-17扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
2022考研12大学科专业排名汇总
发布时间:2019-11-21扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
2023考研政治复习备考资料【珍藏版】
发布时间:2019-11-21扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
考研英语万能模板+必备词汇+范文
发布时间:2019-11-21扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
考研数学一、二、三历年真题整理
发布时间:2019-11-21扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包

添加班主任领资料
添加考研班主任
免费领取考研历年真题等复习干货资料

 推荐阅读
推荐阅读
亲爱的26届考研同学们,对于备战考研英语二的考生来说,掌握有效的复习方法和高质量的备考资料至关重要。2025年考研英语二真题解析作为
来源 : 2025-03-20 08:37:00 关键字 : 考研英语二真题
亲爱的26届考研同学们,对于英语专业的考研生来说,英语专业考研一直是备考重点。通过有效的复习和高质量的学习资料才能确保成功。2025
来源 : 2025-03-19 08:34:00 关键字 : 英语专业考研真题
亲爱的26届考研同学们,考研英语一直是我们备考中的重要一环,高效的备考策略和优秀的学习资料是取得成功的关键。如今,学习资源的电子
来源 : 2025-03-18 08:32:00 关键字 : 英语考研真题电子版
亲爱的26届考研同学们,备战考研需要扎实的英语基础,尤其是翻译部分的备考更是对综合能力的一大挑战。2025年考研英语翻译真题作为最近
来源 : 2025-03-31 08:32:00 关键字 : 考研英语翻译真题
亲爱的26届考研同学们,考研英语作文作为英语考试中的重要组成部分,一直以来都是众多考生感到头疼的部分。如何精准地抓住考点,高效备
来源 : 网络 2025-03-31 08:29:00 关键字 : 2025年考研英语作文真题

 资料下载
资料下载
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
新东方在线考研资料合集
下载方式:微信扫码,获取网盘链接

目录:
1.2013-2023年近10年政数英真题及解析PDF版(新东方)
2.2013-2023年专业课考试历年真题及解析PDF版
3.24考研复习备考资料大合集:大纲+备考资料+词汇书+考前押题+自命题
资料介绍:
1.2013-2023年近10年政数英真题及解析PDF版(新东方)
 、
、
2.2013-2023年专业课考试历年真题及解析PDF版


3.24考研复习备考资料大合集

3.24考研复习备考资料:考研大纲

3.24考研复习备考资料:政数英备考资料+自命题真题

------------------
考研备考过程中,尤其是专业课部分,参考往年的考试真题,对于我们的复习有更好的帮助。北京大学考研真题资料都有哪些?小编为大家进行了汇总。
北京大学考研真题资料-公共课

北京大学考研真题资料-专业课


以上就是关于“北京大学考研真题资料下载(历年汇总)”的整理,更多考研资料下载,请关注微信获取下载地址。
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包
扫码添加【考研班主任】
即可领取资料包

 阅读排行榜
阅读排行榜
 相关内容
相关内容